Medicine has gone through a paradigm shift within the recent years. Less than 200 years ago, there were no vaccines, no treatments and often the only way to prevent catching a disease was self-isolation. Now, we have eradicated diseases like Smallpox, developed MRI machines and even made check-ups possible through our phones. Technology has only made medicine and healthcare services more efficient and is changing the way we look at healthcare. Today, NSTEM will be looking at 5 ways technology is changing medicine.
- Remote Monitoring – The invention of wearable technology, trackers and sensors like FitBits and Apple Watches make the monitoring of vital health signals like heart rate, sleep routine and overall fitness for both the doctor and patient easier. It allows people to track almost every aspect of their health which allows people to take the initiative to make healthy changes within their own lives, saving money spent visiting a doctor.

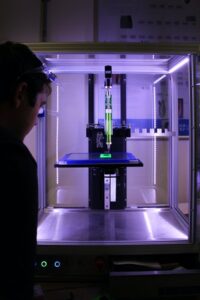
Image credits - 3D Printing – As the demand for organ donors increases, a promising field is 3D printing. This is already integrated into medicine with the 3D rendition of critical areas in the body like the heart and lungs for aspiring doctors to practice on and learn how to operate on a lifelike dummy. As well as that, major strides are being made in the 3D printing of bones, with the development of prosthetic limbs that are altered to fit the patient better and even with 3D printing of organs such as the plastic heart, to extend patients lifespan so they can receive an organ donation, and as technology progresses, they may be able to replace the organ itself.
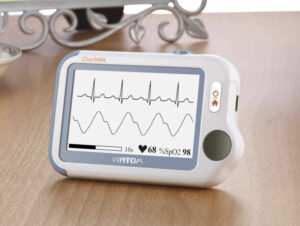
- Medical Tricorder – Almost every doctor wishes they had a device to diagnose and analyse all the vital signs and the potential problems a patient is facing, and it seems even more likely with current developments in technology. The development of the Viatom CheckMe Pro is a huge stride in the achievement of that. It is a palm-sized gadget which can measure ECG, heart rate, oxygen saturation, temperature, blood pressure and more from a few samples from a patient all in one device, saving crucial time for doctors especially in critical situations.

Image credits - Nanotechnology – Nanotechnology is science, engineering, and technology conducted at the nanoscale of 1-100 nm. It is becoming more and more prevalent in medicine as being a precise way to deliver medicine to certain parts of the body, with the invention of PillCam, which monitors the colon and helps diagnose GI bleeding. Even larger strides are being made as MIT “recently created an electronic pill that can be controlled wirelessly and relay diagnostic information or release drugs in response to smartphone commands.”
- Virtual Reality –

Image credits Sure, we know that virtual reality makes for some good horror games but it is becoming more and more prevalent in all different sectors of medicine. Aspiring surgeons and doctors are using VR to practice surgeries and it is being proven to be very effective. According to the Harvard Business Review, a study showed that VR-trained surgeons had a 230% boost in their overall performance compared to other traditionally-trained doctors. As well as that, it is being used more and more as a way for pain management. Women in labour are equipped with VR headsets to visualise soothing landscapes to help them through labour pain and even patients with post-surgical pain or during intense surgeries are seen to have lower pain levels when using VR to distract them from the painful stimuli.
In conclusion, the combination of medicine and technology provides us with better and faster monitoring for both doctors and patients themselves, doctors to gain better experience and even changes to the monitoring and administering of drugs, and even developing new organs. This combination is still developing and at the rapid pace that technology improves, we can hope that there will be continual improvements and changes in the way healthcare and medicine continues to develop.
Written by: Hussam Waseem