There is no other field that goes through as many changes as chemistry. It has gone through the most paradigm shifts and changes of the sciences. The Periodic Table and the model of the atom have changed multiple times throughout the course of history, and even today more and more things are being found out about chemistry and how it works in general society. Chemistry is an ever-changing field and, today, NSTEM will help guide you through the most important of these recent changes.
The biggest breakthroughs within chemistry currently consist of the field of biochemistry. After COVID, there was a major shift towards the importance of biochemistry.

- The Nobel Prize for Chemistry winners Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna were awarded for their work in developing ‘genetic scissors’ which can cut DNA at a specific location and then alter it. The key benefits of this have been to help with the treatments of diseases like sickle cell disease and the Nobel Prize community recognises the gravity of their achievements labelling it as having a “revolutionary impact on the life sciences, contributing to new cancer therapies and may make the dream of curing inherited diseases come true”.
- A new engineering method has been developed by the University of Michigan to generate nanobodies. Nanobodies are small antibody fragments which bind strongly to their target molecules and block their functions. Currently, the antibody or nanobody is suggested and then after long, hard work it is altered and then used for therapeutic purposes. However, this new method by engineering nanobodies with drug-like properties has been a breakthrough, neutralizing the SARS-CoV-2 “more potently than an antibody isolated from an infected patient and a nanobody isolated from an immunized animal.”

- McMaster University designed new DNA-based technology that may replace the need to send results to the lab when visiting the doctor. The DNA-based technology is the same size as a handheld blood-glucose monitor and contains a microchip. It analyses either blood, urine or saliva, and within the chip there are molecules that can detect the specific protein structure of different infections. This is then plugged into a smartphone and returns a diagnosis on the spot, saving all the time that is gone when waiting for lab results, with the maximum amount of time to wait being less than an hour. This is still an early development and can only detect bacterial diseases but has potential to revolutionize medicine and disease detection and prevention especially in an LEDC (Less Economically Developed Country).
Aside from biochemistry, another major field with significant discoveries has been related to climate change and global warming. Chemists have put these problems on their high priority lists and from this we can see significant breakthroughs and developments.

- Bacteria found in rumen, which is a compartment of the cow stomach, have been found to break down plastics. This presents an opportunity to break down plastics that will often remain within the world for over hundreds of years. It has only been done on a lab-scale but upscaling should be easy due to the large amount of rumen present at slaughterhouses. It has been tried on textiles, manufacturing materials and plastic bags.
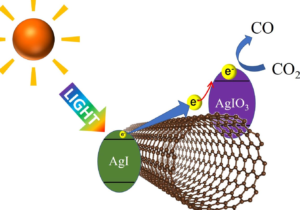
- The Nagoya Institute of Technology has found a way to alleviate global warming by using sunlight. This has been done by using a carbon nanotube and both AgIO3 and AgI on either side of the tube, which are photocatalysts. Photocatalysts use light to provide energy and make a reaction occur. Light is incident on AgI which is transferred to the AgIO3 via the tube and thus CO2 is reduced into carbon monoxide (CO), which could be crucial in lowering CO2 emissions in the atmosphere as they are converted into CO. The issue that they currently face is that CO is a poisonous, toxic and colourless gas which may lead to issues with upscaling.

- The Chinese Academy of Sciences has also found a way to reduce CO2 emissions by using catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol at a low temperature and even more efficiently than commercial catalysts like copper. It uses a catalyst, molybdenum sulfate (MoS2), in a few layers which then activates the reaction at low temperatures and even room temperatures to lead to the creation of methanol. The results of their investigation were compared to using other catalysts like Copper, Zinc Oxide and Aluminium Oxide, which are commercially used but their result of 94.3% was better than the others.
Finally, another interesting area of chemistry has experienced a few significant breakthroughs is called astrochemistry.
- A few months ago, scientists discovered the presence of phosphine in Venus’s atmosphere. Venus has mostly been written off by people as being too hot or too poisonous to support any form of life. However, this discovery of phosphine, which is found on earth with the presence of oxygen-averse microbes, has led scientists to believe it as being a possible signature for life on Venus, yet some scientists are still skeptical about its origins and the validity of the data collected.

- Building a colony on mars has also gained some more fuel through the discovery of a catalyst that destroys perchlorate. Water on Earth is contaminated often by perchlorate, with even higher concentrations of perchlorate in Martian soil, which could mean that food grown there is unsafe to eat. Scientists have often tried to use a molybdenum catalyst for the reduction of perchlorate but often overthought the difficulty, while the team led by University of California Riverside engineers taking inspiration from nature to solve this problem. By mixing a common fertilizer called sodium molybdate, bipyridine to bind the molybdenum, and palladium as a catalyst, all commonly found chemicals, they efficiently broke down the perchlorate in water using hydrogen gas at room temperature with no combustion involved, leaving chloride behind. Coupled with other processes, it has the potential to decontaminate the soil of Mars and even provide oxygen for Mars colonies.
These are just a few of the most interesting chemical breakthroughs that NSTEM has found recently. Chemistry changes everyday with more and more work being published in different fields and journals and it is very interesting to see what happens next. Chemistry is set for even more paradigm shifts in the future!
By Hussam Waseem

